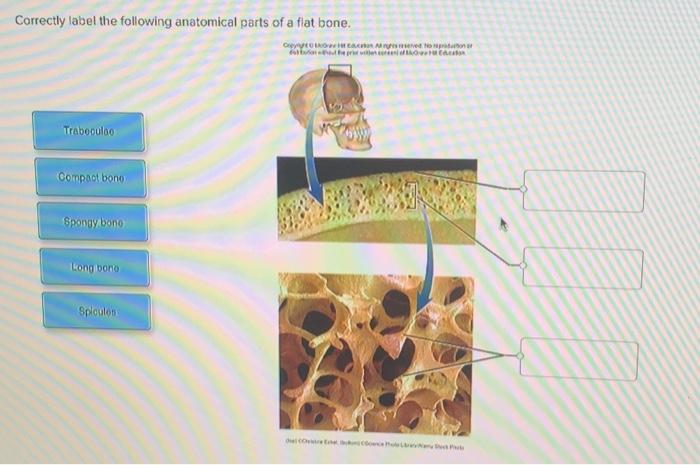
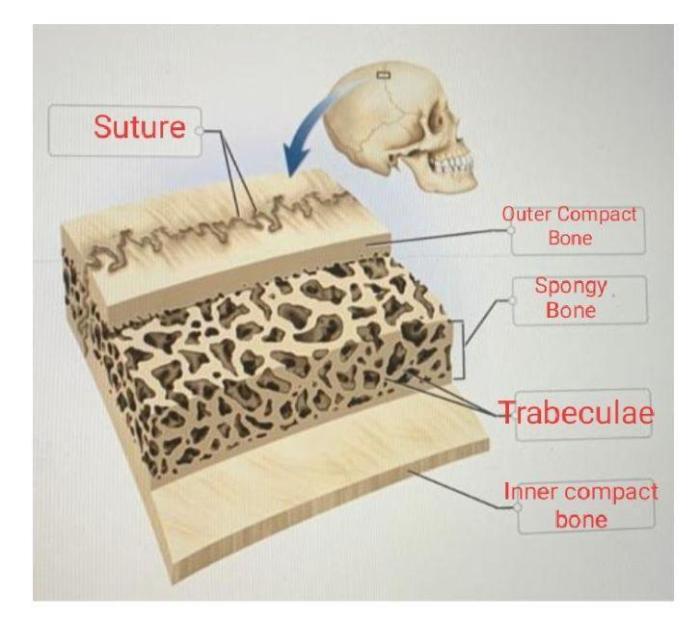
Correctly label the following anatomical parts of a flat bone. – Correctly labeling the anatomical parts of a flat bone is crucial for understanding its structure, function, and clinical significance. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the anatomical regions, identification, structural features, and examples of flat bones in the human body.
Understanding these aspects is essential for medical professionals, students, and anyone interested in human anatomy.
Anatomical Regions of a Flat Bone
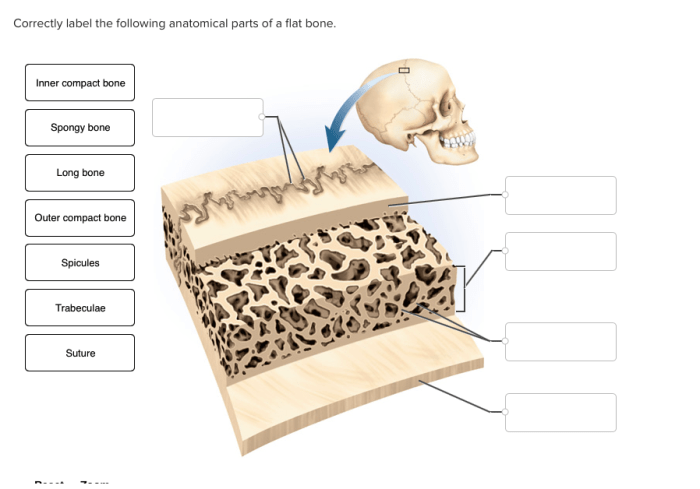
Flat bones are thin and broad, with a compact outer layer and a cancellous inner layer. They provide protection, support, and attachment points for muscles.The anatomical regions of a flat bone include:
- External surface:The outer surface of the bone is covered by a thin layer of periosteum, which is a connective tissue membrane that provides nutrients and oxygen to the bone.
- Internal surface:The internal surface of the bone is lined by endosteum, which is a thin layer of connective tissue that lines the marrow cavity.
- Marrow cavity:The marrow cavity is a central cavity within the bone that contains bone marrow, which produces blood cells.
- Compact bone:The compact bone is the dense outer layer of the bone, which provides strength and protection.
- Cancellous bone:The cancellous bone is the porous inner layer of the bone, which is filled with bone marrow and provides flexibility.
- Epiphyseal line:The epiphyseal line is a thin line that separates the epiphysis from the diaphysis.
- Epiphysis:The epiphysis is the end of the bone that is covered by cartilage.
- Diaphysis:The diaphysis is the shaft of the bone.
Questions and Answers: Correctly Label The Following Anatomical Parts Of A Flat Bone.
What are the main anatomical regions of a flat bone?
The main anatomical regions of a flat bone include the external surface, internal surface, margins, and processes.
How do you identify and label the anatomical parts of a flat bone?
Interactive HTML tables or diagrams with detailed descriptions and illustrations can assist in identifying and labeling the anatomical parts of a flat bone.
What are the key structural features that contribute to the strength and flexibility of flat bones?
Compact bone and cancellous bone contribute to the strength and flexibility of flat bones, providing protection and support while allowing for some degree of flexibility.