Identify the amino acids that give strength to collagen. – Unveiling the molecular underpinnings of collagen’s remarkable strength, this article delves into the specific amino acids that endow this essential protein with its structural integrity, shaping the diverse tissues that constitute our bodies.
Collagen, a ubiquitous protein, plays a pivotal role in maintaining the structural integrity of connective tissues, including skin, bones, and cartilage. Its strength and stability stem from a unique triple-helical structure, stabilized by specific amino acid interactions. This article explores the key amino acids responsible for collagen’s strength, examining their roles and interactions within the collagen molecule.
Key Amino Acids in Collagen Strength
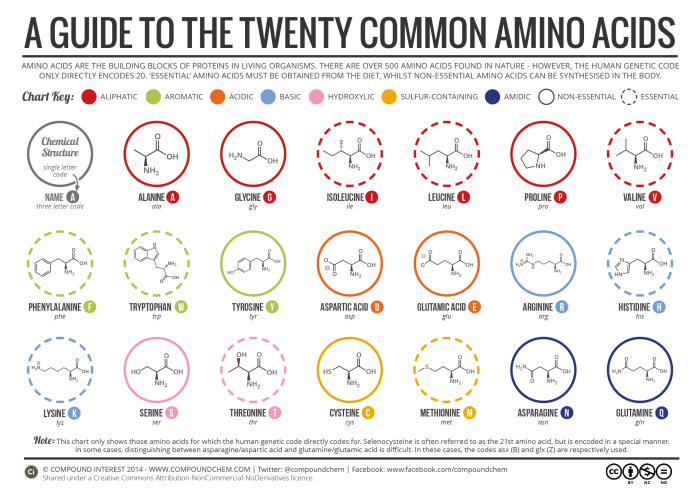
Collagen, a structural protein found in various connective tissues, derives its strength from specific amino acids that contribute to its unique structure and stability. These key amino acids are:
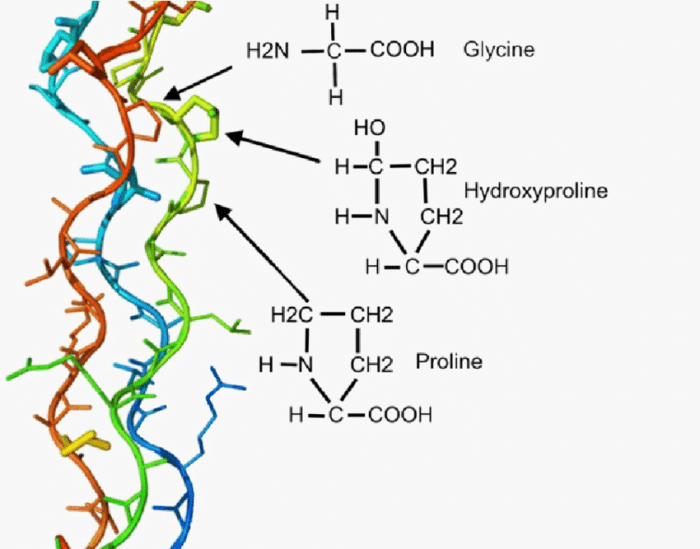
- Glycine: The most abundant amino acid in collagen, glycine allows for tight packing of collagen molecules.
- Proline and hydroxyproline: These amino acids provide rigidity and stability to the collagen triple helix.
- Hydroxylysine and hydroxyproline: These hydroxylated amino acids facilitate cross-linking between collagen molecules, enhancing strength.
Amino Acid Interactions and Collagen Structure
The formation of the collagen triple helix involves specific interactions between amino acids. Glycine residues, due to their small size, fit into the center of the helix, while proline and hydroxyproline stabilize the structure by forming hydrogen bonds. Hydroxylysine and hydroxyproline facilitate cross-linking through covalent bonds, providing additional strength.
Collagen Strength in Different Tissues
Collagen strength varies across tissues due to differences in amino acid composition and structure. For instance, skin collagen is more resistant to stretching than cartilage collagen. This variation arises from the presence of different collagen types, each with unique amino acid sequences and cross-linking patterns.
Collagen Strength and Disease
Mutations in collagen genes can affect amino acid composition and structure, leading to weakened collagen and diseases such as osteogenesis imperfecta and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. These diseases highlight the crucial role of collagen strength in maintaining tissue integrity.
Applications of Collagen Strength, Identify the amino acids that give strength to collagen.
Collagen’s strength finds applications in various fields:
- Biomaterials: Collagen-based materials are used in medical implants and tissue engineering due to their biocompatibility and strength.
- Cosmetics: Collagen is incorporated into skincare products for its ability to enhance skin elasticity and reduce wrinkles.
Q&A: Identify The Amino Acids That Give Strength To Collagen.
What is the primary amino acid responsible for collagen’s strength?
Glycine is the primary amino acid responsible for collagen’s strength, as it facilitates the formation of the collagen triple helix.
How do hydroxyproline and proline contribute to collagen’s strength?
Hydroxyproline and proline stabilize the collagen triple helix by forming hydrogen bonds and creating steric hindrance, respectively.