Welcome to the definitive guide to right triangles! This comprehensive resource, ch 7 notes right triangles answer key, will equip you with the knowledge and techniques to conquer any right triangle problem with confidence. From understanding the basics of the Pythagorean theorem to mastering advanced concepts like the Law of Sines and Cosines, this guide has got you covered.
Throughout this guide, we will explore the fascinating world of right triangles, their properties, and their applications in real-world scenarios. Whether you’re a student seeking to excel in geometry or a professional seeking to enhance your problem-solving skills, this guide is your ultimate companion.
Right Triangle Properties
Right triangles, characterized by their 90-degree angle, exhibit unique relationships between their sides and angles. The Pythagorean theorem, a fundamental property, states that the square of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
This theorem serves as a cornerstone for solving right triangle problems.
Furthermore, right triangles possess trigonometric ratios that link the sides and angles. Sine, cosine, and tangent are the primary ratios, each defined by the ratio of specific sides to each other. For special angles (30°, 45°, 60°), these ratios assume specific values, providing a valuable tool for solving problems.
Solving Right Triangle Problems
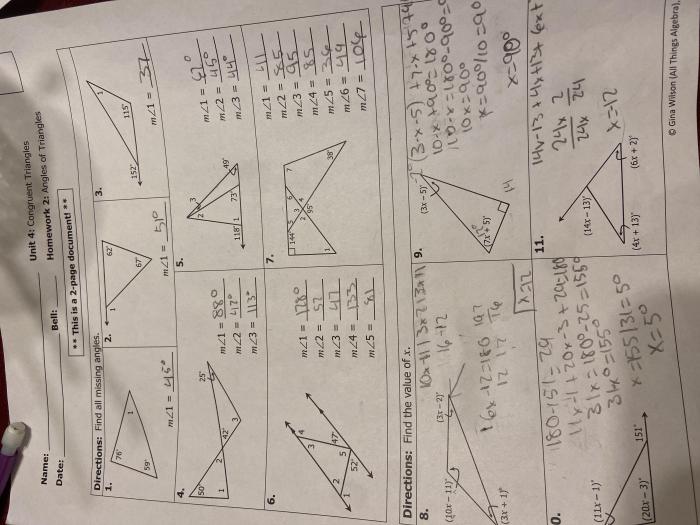
Solving right triangle problems involves utilizing the Pythagorean theorem and trigonometric ratios. By understanding these relationships, it becomes possible to determine unknown sides, angles, or both. The process typically involves identifying the given information, applying the appropriate theorem or ratio, and solving for the unknown quantity.
Special right triangles, such as the 30°-60°-90° and 45°-45°-90° triangles, offer simplified calculations due to their predefined side and angle relationships.
Applications of Right Triangles
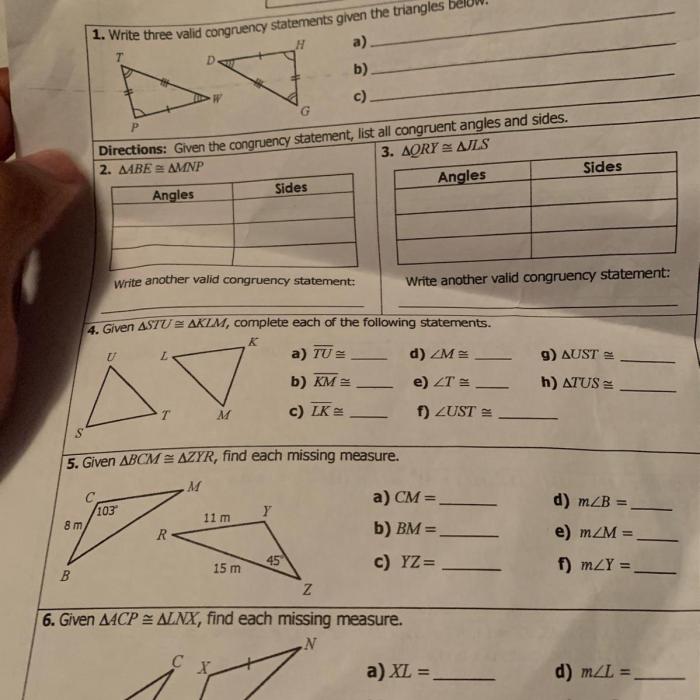
Right triangles find widespread applications in real-world scenarios, particularly in architecture, engineering, and navigation. They enable the calculation of distances, heights, and angles in practical situations. For instance, in architecture, right triangles are used to determine roof pitches and calculate the height of buildings.
In engineering, they aid in structural analysis and design.
Trigonometry, based on right triangle principles, plays a crucial role in surveying and astronomy. It allows for the precise measurement of distances and angles, facilitating the creation of maps and the study of celestial bodies.
Advanced Right Triangle Concepts: Ch 7 Notes Right Triangles Answer Key
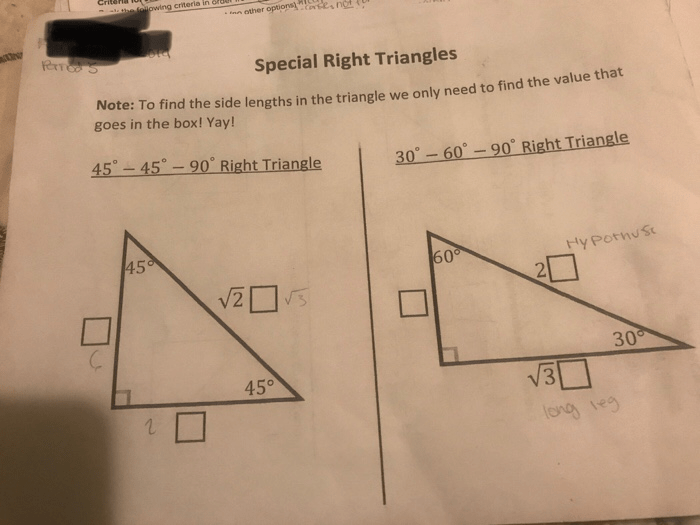
Beyond the basic properties, advanced right triangle concepts delve into the unit circle and inverse trigonometric functions. The unit circle establishes a connection between right triangles and circular functions, enabling the definition of sine, cosine, and tangent for all angles.
Inverse trigonometric functions (arcsine, arccosine, arctangent) are essential for solving problems where the angle is known, and the side needs to be determined. Additionally, the Law of Sines and Law of Cosines extend the principles of right triangles to oblique triangles, allowing for the solution of more complex problems.
Key Questions Answered
What is the Pythagorean theorem?
The Pythagorean theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
What are trigonometric ratios?
Trigonometric ratios are ratios of the lengths of the sides of a right triangle. The three main trigonometric ratios are sine, cosine, and tangent.
How can I use right triangles to solve real-world problems?
Right triangles can be used to solve a variety of real-world problems, such as finding the height of a building, the distance to a star, or the angle of a slope.