Geometry chapter 7 review answers – Get ready to conquer Geometry Chapter 7 with our comprehensive review answers! This guide will take you on a captivating journey through angles, triangles, and quadrilaterals, empowering you to solve problems like a pro. Dive in and unlock the secrets of geometry today!
In this guide, we’ll delve into the key concepts, problem-solving techniques, theorems, and formulas covered in Chapter 7. We’ll also explore real-world applications of geometry and its interdisciplinary connections. Get ready to expand your knowledge and master the world of shapes!
Chapter 7 Review Concepts
Chapter 7 delves into the fascinating world of geometry, exploring fundamental concepts that shape our understanding of shapes and their relationships. These concepts, including angles, triangles, and quadrilaterals, serve as building blocks for various real-world applications, from architecture and engineering to art and design.
Angles, measured in degrees, represent the amount of rotation between two lines. Understanding angles is crucial in fields like carpentry, where precise measurements are essential for constructing sturdy structures. Triangles, with their three sides and three angles, are the simplest polygons.
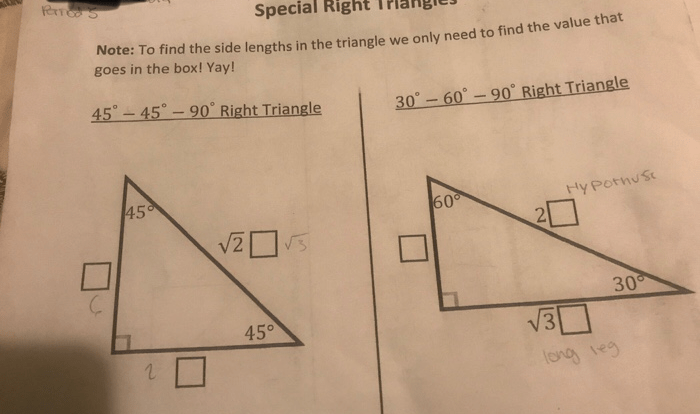
Their properties, such as the Pythagorean theorem, are widely used in fields like surveying and navigation.
Quadrilaterals
Quadrilaterals, polygons with four sides, exhibit diverse shapes and properties. Parallelograms, with their opposite sides parallel, find applications in tiling and flooring. Trapezoids, with one pair of parallel sides, are commonly found in roof designs and bridge construction. Rectangles, with four right angles, serve as the basis for many architectural structures, while squares, with four equal sides, are renowned for their symmetry and stability.
Problem-Solving Techniques: Geometry Chapter 7 Review Answers
Conquering geometry problems requires a systematic approach. By implementing effective problem-solving techniques, you’ll unravel geometric puzzles with confidence. This section delves into strategies for identifying relevant information, applying geometric principles, and comparing different problem-solving approaches.
Identifying Relevant Information
The key to solving geometry problems lies in understanding the problem statement. Carefully read the problem and identify the given information, what is being asked, and any diagrams or figures provided. Highlight important details and draw sketches to visualize the problem.
Applying Geometric Principles
Geometry is a treasure trove of theorems, postulates, and formulas. To solve problems effectively, it’s crucial to apply these principles. Remember the Pythagorean theorem, area and volume formulas, and properties of shapes. Use these principles as building blocks to construct your solutions.
Problem-Solving Approaches
There are various problem-solving approaches to tackle geometry problems. Each approach has its strengths and weaknesses. Explore the table below for a comparison:
| Approach | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Analytical Approach | Using algebraic equations and formulas to solve for unknown variables. | – Precise and systematic
|
– Can be time-consuming
|
| Geometric Approach | Applying geometric properties and theorems to visualize and solve problems. | – Intuitive and visual
|
– May not be suitable for complex algebraic problems
|
| Guess-and-Check Approach | Making educated guesses and checking the results until a solution is found. | – Quick and simple
|
– Not reliable for complex problems
|
Remember, the best approach depends on the specific problem you’re facing. Choose the one that resonates with your understanding and allows you to solve the problem efficiently.
Theorems and Formulas
In Chapter 7, we encountered a wealth of theorems and formulas that serve as essential tools for solving geometry problems. These mathematical principles provide a framework for understanding and manipulating geometric shapes and their properties.
Applying these theorems and formulas requires a systematic approach. First, identify the relevant theorem or formula that applies to the problem at hand. Next, carefully examine the given information and determine the values of any variables involved. Finally, substitute these values into the formula and perform the necessary calculations to arrive at the solution.
Important Theorems and Formulas
- Triangle Sum Theorem:The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is 180 degrees.
- Exterior Angle Theorem:The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of the two opposite interior angles.
- Pythagorean Theorem:In a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
- Area of a Triangle:The area of a triangle is equal to half the base multiplied by the height.
- Area of a Parallelogram:The area of a parallelogram is equal to the product of the base and the height.
- Area of a Circle:The area of a circle is equal to πr², where r is the radius of the circle.
- Circumference of a Circle:The circumference of a circle is equal to 2πr, where r is the radius of the circle.
Infographic: Key Theorems and Formulas
[Insert an infographic here that summarizes the key theorems and formulas introduced in Chapter 7.]
Practice Problems
This section provides a set of practice problems that cover the concepts and skills from Chapter 7. These problems are organized into sections based on difficulty level, with step-by-step solutions to demonstrate the problem-solving process.
Easy Problems
- Find the area of a triangle with a base of 10 cm and a height of 8 cm.
- Find the volume of a rectangular prism with a length of 5 cm, a width of 3 cm, and a height of 2 cm.
- Find the surface area of a cube with a side length of 4 cm.
Medium Problems, Geometry chapter 7 review answers
- Find the volume of a cone with a radius of 5 cm and a height of 10 cm.
- Find the surface area of a sphere with a radius of 6 cm.
- Find the volume of a cylinder with a radius of 4 cm and a height of 8 cm.
Hard Problems
- Find the volume of a pyramid with a square base of side length 10 cm and a height of 15 cm.
- Find the surface area of a hemisphere with a radius of 8 cm.
- Find the volume of a frustum of a cone with radii of 6 cm and 10 cm and a height of 12 cm.
Applications in Other Disciplines
Geometry, the study of shapes and their relationships, plays a crucial role in various disciplines beyond mathematics. Its concepts and principles find widespread applications in architecture, engineering, and art, enabling professionals to design, construct, and create masterpieces that both serve functional purposes and captivate the human eye.
Let’s delve into specific examples of how geometry manifests itself in these fields:
Architecture
- Building Design:Architects utilize geometry to determine the shape, size, and proportions of buildings, ensuring structural stability, functionality, and aesthetic appeal.
- Interior Design:Geometry guides the placement of furniture, walls, and other elements within a space, optimizing flow and maximizing space utilization.
- Facade Design:Geometric patterns and shapes are incorporated into building facades, creating visually striking and iconic structures.
Engineering
- Civil Engineering:Geometry underpins the design of bridges, roads, and other infrastructure, ensuring structural integrity and load-bearing capacity.
- Mechanical Engineering:Geometric principles are applied in the design of machinery, engines, and other mechanical systems, optimizing efficiency and performance.
- Aerospace Engineering:Geometry plays a vital role in designing aircraft and spacecraft, ensuring aerodynamic efficiency and stability.
Art
- Painting and Drawing:Artists use geometry to create perspective, depth, and composition in their works, conveying a sense of space and realism.
- Sculpture:Sculptors employ geometric shapes and forms to create three-dimensional artworks, exploring volume, balance, and harmony.
- Design:Geometric patterns and motifs are widely used in graphic design, textiles, and product design, adding visual interest and functionality.
Question Bank
What are the key concepts covered in Geometry Chapter 7?
Angles, triangles, and quadrilaterals.
How can I improve my problem-solving skills in geometry?
Practice regularly and apply geometric principles to real-world situations.
What are the most important theorems and formulas in Chapter 7?
Pythagorean Theorem, Angle Sum Theorem, Area and Perimeter formulas.